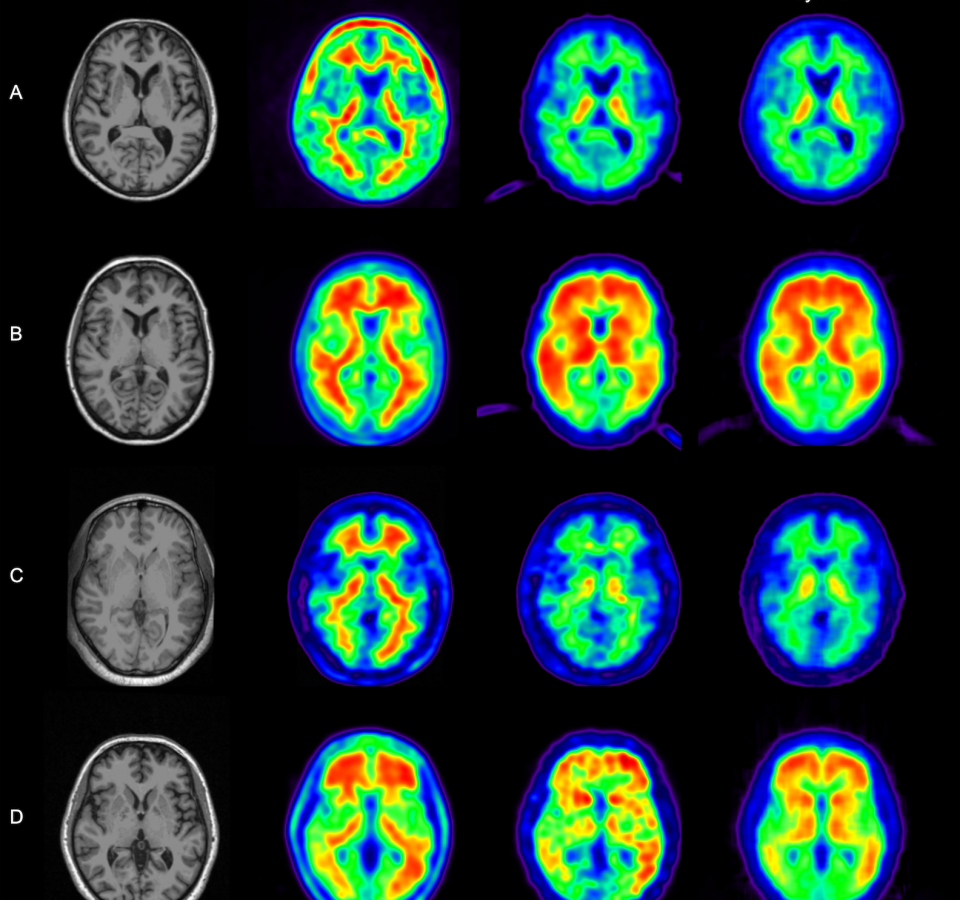
Amyloid PET is an in vivo technology used to quantify beta-amyloid deposition in the brain. However, use of multiple amyloid tracers with varied characteristics compounded by processing variabilities poses significant challenges to interpret or combine results from cross-center studies, and to define common positivity threshold. Here, we developed an encoder-decoder based deep model as a harmonization strategy to render imputed amyloid PET images of one amyloid tracer to the images of another. The model discovered the voxel-wise nonlinear associations between the input and output images which significantly improved agreements of amyloid burden measurements from different tracers.
Age is the biggest risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Substantial efforts to extract age signatures from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain have achieved impressive accuracy and demonstrated these signatures were altered by neurological disorders including AD. In this work, we develop a deep learning model to characterize brain age signatures and examine their variation over the AD continuum.